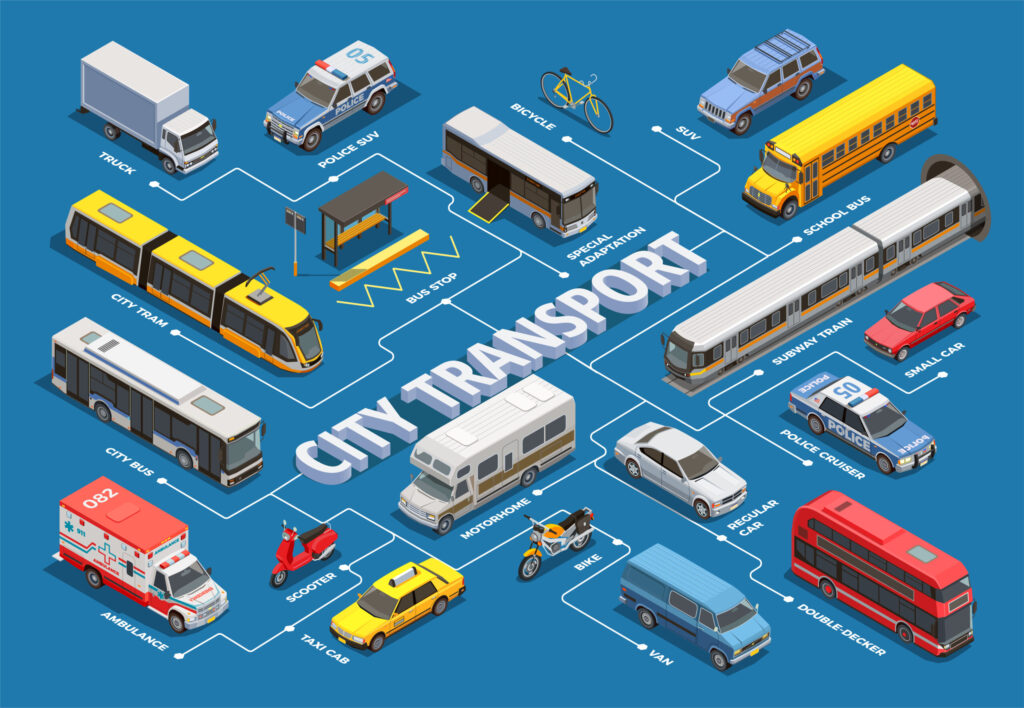
In the rapidly evolving landscape of urban life, public transportation systems play a crucial role in how we navigate cities. As urban populations grow, the demand for efficient and sustainable transportation options becomes increasingly vital. Public transportation alleviates traffic congestion and reduces environmental impact by minimizing private vehicle use. By enhancing connectivity and accessibility, these systems foster community and ensure equitable participation in urban experiences. This article explores the numerous benefits of public transportation systems and their transformative impact on urban life.
Benefits of public transportation systems
Public transportation systems provide numerous benefits that significantly enhance urban life:
Reducing traffic congestion
Public transportation systems help alleviate traffic congestion by offering alternatives to private vehicles, leading to improved travel times and reduced frustration during commutes.
Environmental protection
These systems play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability. By encouraging the use of buses and trains, cities can significantly lower carbon emissions and air pollution, contributing to cleaner urban environments.
Cost savings
Utilizing public transportation can lead to substantial savings for individuals and families by reducing expenses associated with car ownership, such as fuel, insurance, and parking.
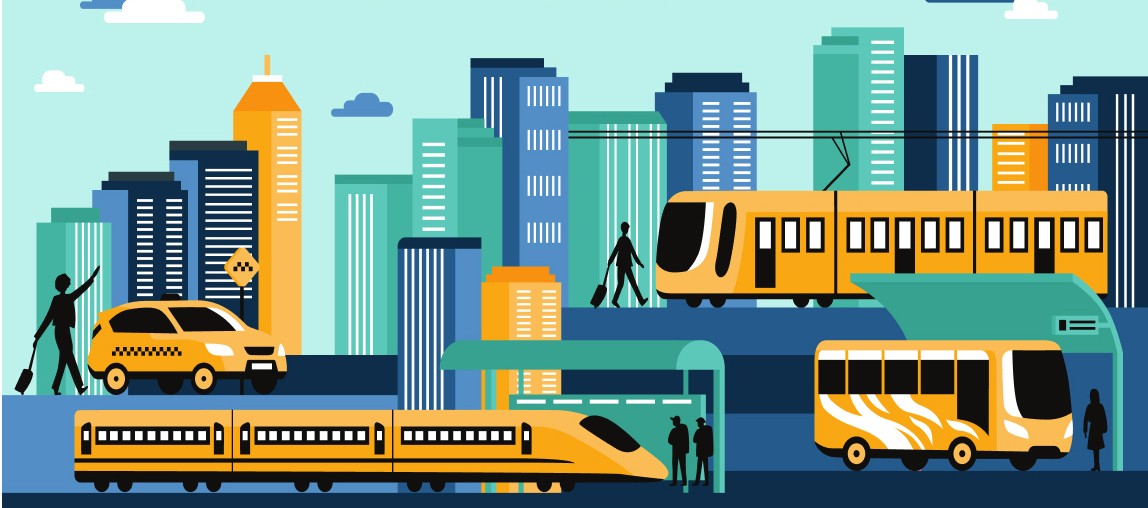

Accessibility for all
Public transportation systems enhance accessibility for diverse populations, ensuring that everyone can reach essential services and opportunities, regardless of age or income level.
Economic development
Investing in public transportation stimulates local economies by increasing foot traffic for businesses and creating jobs in both the transportation sector and related industries.
Improved quality of life
Ultimately, public transportation contributes to a better quality of life by reducing travel times, lowering costs, and enabling residents to engage more in community activities and leisure.
Types of public transportation systems
Public transportation systems encompass various modes designed to meet the diverse needs of urban populations. Buses are widely used, operating on designated routes and schedules, making them accessible and flexible for many passengers. Subway systems provide rapid transit in densely populated areas, transporting large numbers of passengers quickly and efficiently while reducing surface-level congestion. Trams and light rail offer frequent service in urban settings, ideal for short-distance travel and promoting pedestrian-friendly environments.
Commuter trains connect suburban and rural areas to urban centers, helping reduce traffic congestion over longer distances. In cities with waterways, ferries serve as a unique mode of transportation, connecting different parts of the region while providing scenic views. Additionally, ride-sharing services and microtransit solutions enhance public transportation by filling coverage gaps and offering flexible, on-demand options.
In summary, public transportation systems are diverse, each serving vital roles in urban mobility. By providing options like buses, subways, ferries, and ride-sharing, cities can create efficient and accessible transportation networks that cater to their residents’ needs.
Challenges and solutions for public transportation systems
Public transportation systems encounter various challenges that can affect their effectiveness. However, several innovative solutions can address these issues.
Budget constraints
Challenge: Limited funding often leads to inadequate services and aging infrastructure.
Solution: Cities can explore alternative funding sources, such as public-private partnerships and grants, while implementing fare structures that reflect demand to generate additional revenue.

Safety and security issues
Challenge: Safety concerns, including crime and harassment, can deter users.
Solution: Enhancing safety measures through increased police presence, surveillance systems, and public education campaigns can improve user confidence.
Accessibility challenges
Challenge: Many systems lack accommodations for individuals with disabilities.
Solution: Upgrading infrastructure, such as ramps and elevators, and training staff to assist passengers can improve accessibility.
Ensuring sustainability
Challenge: The environmental impact of public transportation can be significant due to reliance on fossil fuels.
Solution: Transitioning to electric and hybrid vehicles, promoting renewable energy, and developing eco-friendly infrastructure can enhance sustainability.
System integration
Challenge: Lack of coordination between different transit modes can lead to inefficiencies.
Solution: Promoting integrated transportation networks, including apps for real-time information and unified fare systems, can simplify user experience.
Smart initiatives in public transportation
The integration of smart technologies into public transportation systems has revolutionized urban mobility by enhancing efficiency, safety, and user experience. One of the most significant advancements is the implementation of real-time tracking and information systems. Utilizing GPS and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, these systems provide passengers with live updates on vehicle locations through mobile apps and digital signage at stations. This transparency allows travelers to plan their journeys more effectively, reduces waiting times, and ultimately improves overall satisfaction, encouraging greater ridership.
Another important initiative is the adoption of contactless payment solutions, which streamline fare collection. Passengers can use smartphones, smart cards, or wearable devices to pay for their rides, enhancing convenience and reducing the reliance on cash transactions. This not only speeds up the boarding process but also makes public transportation more efficient. Additionally, predictive analytics and demand-responsive transit (DRT) systems leverage big data to analyze ridership patterns, allowing agencies to adjust services in real time. DRT systems optimize routes by matching passengers with available vehicles, improving service delivery, particularly in underserved areas.
Smart traffic management systems further enhance public transportation efficiency by using sensors and data analytics to monitor traffic conditions. These systems can optimize traffic signals to prioritize public transportation vehicles at intersections, reducing delays and improving transit speed. Integrating traffic management with public transportation leads to a smoother overall experience for both commuters and drivers. Moreover, many smart initiatives focus on sustainability, including the implementation of electric and hybrid vehicles, promoting bike-sharing programs, and developing pedestrian-friendly infrastructure.
Finally, integrated mobility platforms represent a significant leap forward in urban transit solutions. These platforms combine various modes of transportation-such as buses, trains, bikes, and ride-sharing-into a single app. Users can plan multimodal journeys, purchase unified tickets, and access real-time information, creating a seamless transit experience. In conclusion, smart initiatives in public transportation are transforming urban mobility by leveraging technology to create more responsive, user-friendly, and environmentally sustainable systems that meet the evolving needs of residents.
In conclusion, public transportation systems play a crucial role in enhancing urban life by providing accessible, efficient, and sustainable mobility solutions. They not only connect individuals to essential services, jobs, and recreational activities but also foster community engagement and reduce traffic congestion and environmental impact. As cities continue to grow and evolve, investing in and modernizing public transportation systems is essential for meeting the demands of urban populations.
By embracing smart technologies, improving infrastructure, and prioritizing inclusivity, cities can create robust public transportation networks that promote economic growth, social equity, and a higher quality of life for all residents. Ultimately, well-designed public transportation systems are key to building livable, vibrant cities that enhance the overall urban experience.