In recent years, misinformation has emerged as a significant issue in international politics, influencing narratives and shaping public opinion worldwide. The rise of digital communication and social media has made it easier for false information to spread, blurring the lines between fact and fiction. This article explores the causes and impacts of misinformation in international politics and emphasizes the urgent need for effective countermeasures to safeguard democratic processes and informed decision-making.
Causes and motivations of misinformation
Misinformation arises from various causes and motivations, significantly impacting how information is consumed and understood in the context of international politics. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to combat misinformation effectively.
Political manipulation
One of the primary motivations behind the dissemination of misinformation is political manipulation. Political actors may intentionally spread false information to sway public opinion, undermine opponents, or create confusion. This tactic can be seen in election campaigns, where misleading narratives can alter voter perceptions and behaviors.
Economic gain
Misinformation can also be driven by economic interests. Content creators and media outlets may generate sensationalized or misleading stories to attract clicks, views, and ad revenue. This profit-driven motive can lead to the prioritization of sensationalism over accuracy, contributing to the overall spread of misinformation.

Social identity and groupthink
Social dynamics play a significant role in the spread of misinformation. Individuals often seek information that aligns with their pre-existing beliefs, leading to confirmation bias. This phenomenon can create echo chambers, where misinformation is reinforced within like-minded communities, further entrenching false narratives and perpetuating their spread.
Lack of media literacy
In conclusion, misinformation in international politics poses a significant threat to informed decision-making and global stability. As false information spreads rapidly across digital platforms, it influences public opinion, disrupts diplomatic relations, and undermines democratic processes. Addressing misinformation in international politics requires a coordinated effort involving technology, education, and policy reforms to create a more transparent and accountable information environment, ensuring that truth prevails in global political discourse.
Rapid information spread
The speed of information dissemination in the digital age is another contributing factor. Social media platforms and messaging apps enable rapid sharing of content, making it easy for misinformation to spread quickly before it can be fact-checked or debunked. This immediacy can amplify the impact of false narratives, often leading to widespread acceptance before corrections can be made.
Emotional appeal
Misinformation in international politics often leverages emotional appeal to engage audiences. Content that triggers strong emotions, such as fear, anger, or outrage, is more likely to be shared and believed, regardless of its accuracy. This emotional manipulation is a powerful driver for the spread of misinformation in international politics, particularly in politically charged environments.
By understanding the causes and motivations behind misinformation, stakeholders can develop targeted approaches to address its spread. These strategies will ultimately help foster a more informed and balanced public discourse in international politics.
Classification of misinformation
Misinformation can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and purposes. Disinformation involves the deliberate spread of false information intended to deceive, often used for political manipulation. Examples include fake news articles and misleading social media posts that aim to confuse audiences.
Another category is misleading information, which distorts or misrepresents facts, creating a skewed perception of reality. This can include cherry-picked statistics or manipulated quotes. Additionally, fabricated news refers to entirely made-up content designed to attract attention without any factual basis. Understanding these classifications is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat misinformation in international politics.

Impact on political decision-making
Misinformation can have profound effects on political decision-making, often leading to misguided policies and actions. When false or misleading information spreads, it can distort public opinion, causing voters and leaders to make decisions based on inaccurate data. This, in turn, influences elections, public debates, and the development of policies that may not align with the actual needs or desires of the population.
In the international sphere, misinformation can strain diplomatic relations. Countries may react to false narratives or manipulated reports, leading to conflicts or miscommunication between nations. For instance, misinformation campaigns targeting foreign governments or international organizations can provoke tensions, disrupt alliances, or foster distrust, ultimately affecting global stability and cooperation.
Countermeasures against misinformation
Addressing misinformation in international politics requires a multi-faceted approach involving technology, education, and policy changes. One effective strategy is promoting media literacy, which helps individuals critically assess the reliability of information sources. By equipping people with the skills to identify fake news and verify facts, they become less vulnerable to misinformation in international politics, improving the quality of public discourse.
Fact-checking organizations and automated tools are also essential in combating misinformation. Independent fact-checkers and AI-driven algorithms can quickly debunk false claims, providing accurate information to counter misleading narratives. Social media platforms play a crucial role by flagging or removing content that violates misinformation guidelines, helping to limit the spread of misinformation.
Finally, government policies can support these efforts through regulation and collaboration with tech companies, ensuring transparency and accountability in the information ecosystem. Governments can establish clear guidelines for managing misinformation in international politics while protecting free speech and promoting responsible media consumption.
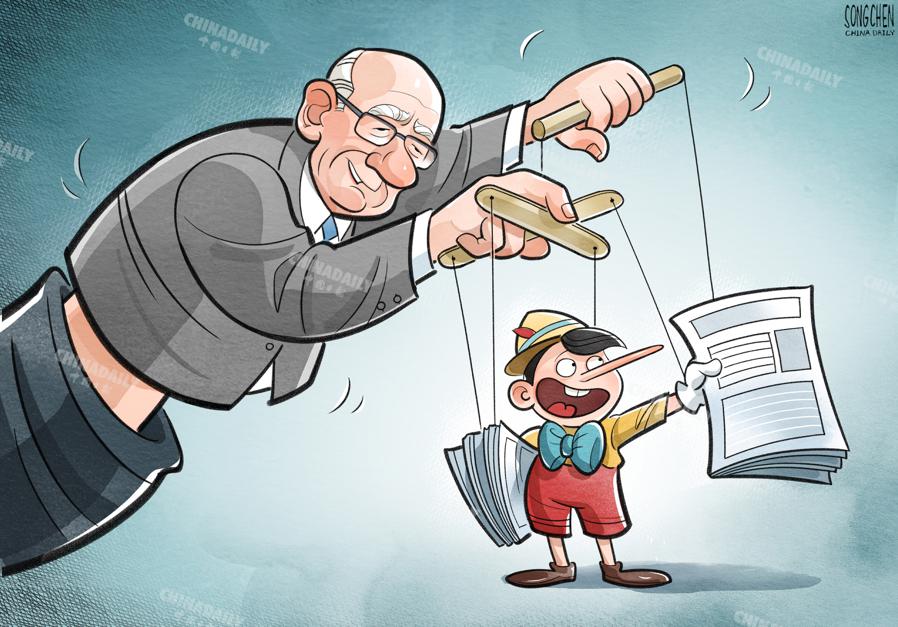

Role of technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in both the spread and mitigation of misinformation. On one hand, social media platforms and digital communication tools have made it easier for false information to spread rapidly, reaching large audiences in a short time. Algorithms often prioritize sensational content, further amplifying misinformation.
On the other hand, technology also offers solutions. AI-powered fact-checking tools and content moderation systems help identify and flag misleading information. Additionally, data analytics can track misinformation patterns, enabling platforms and governments to respond more effectively to its spread.
In conclusion, the surge of misinformation in international politics poses a significant threat to informed decision-making and global stability. As false information spreads rapidly across digital platforms, it influences public opinion, disrupts diplomatic relations, and undermines democratic processes. Addressing this issue requires a coordinated effort involving technology, education, and policy reforms to create a more transparent and accountable information environment, ensuring that truth prevails in international discourse.