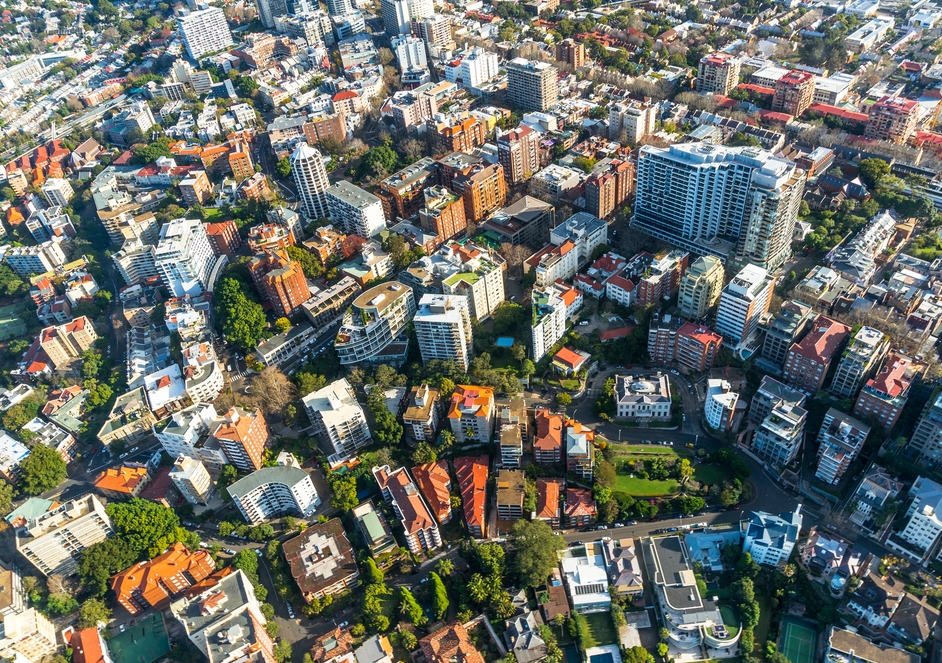
A new business partnership between UNSW, PEXA and Frontier SI launches a data-driven toolkit that quickly calculates property valuations to inform urban development. The toolkit, hosted by new company Slate Analytics, allows users to visualize various infrastructure and planning scenarios and their effect on surrounding property values. It will facilitate data-driven solutions to support better urban planning.
The digital toolkit, called Rapid Analytics Interactive Scenario Explorer (RAISE), uses big data, artificial intelligence and advanced analytics to calculate property valuations in the Australian residential real estate market. Its ability for interactive and what-if scenarios is an industry first for assistance system planning.
RAISE provides a cyber-secure, scalable and commercially viable solution that reduces the risks and costs associated with land value analysis, he says.
“This new business partnership combines PEXA’s expertise in data and digital property regulations, and Frontier SI’s specialization in spatial mapping and geodesy with UNSW’s cutting-edge research in data science and future of our cities to provide a world-class platform,” said Pettit.
Read more: Why bike lanes should be the fast lane for cities
Scott Butterworth, Chief Data and Analytics Officer at PEXA, said, “With its evidence-based scenario modeling, RAISE will revolutionize our approach to urban planning and development. It could also prove very beneficial for the Australian lending community, potentially speeding up the mortgage approval process on behalf of Australian homebuyers. PEXA is excited to lead this company, serving real-world needs. »
The Digital Toolkit is the result of a long-standing research partnership between Frontier SI and UNSW CFRC.
Graeme Kernich, CEO of FrontierSI, says, “Through Slate Analytics, FrontierSI and UNSW have realized their vision of bringing cutting-edge AI to the real estate appraisal products and services space. PEXA’s investment will be key to advancing this vision and expanding the impact this capability will have for Australia and beyond.
The firm builds on previous research with UNSW’s CFRC, Frontier SI, Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Liverpool City Council, NSW Office of the Valuer General and property data management company Omnilink, which was funded by an Australian Government Cooperative Research Centers Project (CRC-P) grant.
A new business partnership between UNSW, PEXA and Frontier SI launches a data-driven toolkit that quickly calculates property valuations to inform urban development.
The toolkit cleans, links and integrates various geospatial and real estate data from trusted government databases and industry partners, including sources such as the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), Geoscape, Valuer General data and transport, education and crime statistics agencies.
It includes a real estate market dashboard developed in response to COVID-19 which provides a daily snapshot of real estate market performance compared to before the pandemic. It features an interactive map of Australia, identifying COVID case numbers based on data from state health departments.
The dashboard provides charts and tables of key real estate market metrics, including median house prices, auction clearance rates, home value index and ASX 200 real estate sector performance , to help government, industry and communities understand the impacts COVID-19 is having on the real estate market.
The toolbox has been used in recent search assess the proposed high-speed rail network on the east coast of Australia. He revealed that the growth in land value around high-speed stations, estimated at $140 billion, could be used to fund the network.
“A significant part of this sum could be spent on financing its construction and supporting the creation of livable and vibrant cities and regions,” says Professor Pettit.
Read more: UNSW launches Cities Institute to help sustain our cities
Understand the influence of infrastructure provision on property values
One of its aims is to improve users’ understanding of land economics, in particular the influence that infrastructure provision and other key variables play on land values, Prof Pettit says.
The tool considers structural attributes, such as building quality, age and size; neighborhood characteristics, such as crime levels and socio-economic profile; and accessibility, such as the nearest transport links, employment centers and services.
It is accessible through a web browser allowing multiple users in various locations to compare and analyze different scenarios. Users can change the tool’s key assumptions, such as access to transportation, schools, hospitals, and zoning plans, and map their effect on property values.
For example, users can drag and drop new train stations into urban areas and predict the anticipated value increase (rise in value) on surrounding properties associated with the accessibility benefits of improved transportation infrastructure.
“New and improved transportation – including new stations, faster trips, more frequent trips, improved services or higher volume services – can connect residents to jobs and services and also connect businesses to markets. workforce, suppliers and customers,” says Professor Pettit. “As such, residents and businesses are expected to pay a premium for properties served by this infrastructure.”

The toolkit has been used in recent research evaluating the proposed high-speed rail network on the east coast of Australia. Image: Shutterstock
Governments want to measure value uplift to determine the viability of using value capture (taxing that uplift) to fund current or future transportation infrastructure projects through policies such as developer fees, stamp duty, land tax and improvement tax, he says.
“Value capture is, essentially, a tax on the increase in land value associated with new or upgraded infrastructure, and these taxes can be used to offset infrastructure costs and fund supporting initiatives, such as new stock or increasing the stock of affordable housing.”
There has been renewed national political interest in value capture in Australia in the debate around the National Settlement Strategy as well as the Smart cities map (2016) and the Greater Sydney Metropolitan Planning Strategy (2018), and internationally, he says.
“The expense involved in engaging specialist valuation consultants means that fewer options are generally explored by planners and decision makers, and effective value capture mechanisms are rarely used in Australian infrastructure planning,” says- he.
UNSW will retain a stake in the new venture, supporting it with ongoing research and development.
“The tool makes an important contribution to building more equitable and productive future cities, helping planners, councils and governments to maximize investments to achieve the best results, including better public transport, green spaces and more affordable housing stock – for the whole community,” says Professor Pettit.
Read more: Family apartments are the key to a compact city
Utility aligned to co-design model with end-user expectations
RAISE was co-designed through a series of workshops with research partners, state government assessors, and local government planners to ensure that its functionality and user experience match end-user expectations.
The workshops evaluated rapid prototypes to optimize the design based on its data inputs, modeling and scenario formulation and visualization, interface and workflow. Feedback shaped further development, extending the tool’s core functionality, model and data integration, and collaborative functionality through a series of iterations.
For example, stakeholder feedback in co-design workshops prompted the introduction of school quality indicators into the modelling, Prof Pettit says. Properties in the watersheds of high-performing schools, as measured by NAPLAN results, were found to be more valued.
The need for digital technologies, such as data-driven scenario tools, will continue to grow with rapid urbanization and global population growth, however, the inherent complexity of big data as well as the diversity of actors and conflicting agendas mean that tools work best in tandem. with expert knowledge, he says.
“These tools and technologies work hand-in-hand with key planners and decision-makers who shape the future of the city… We all strive for more livable cities, more sustainable, more resilient, more productive cities. [and] inclusive cities. The tools are used to support these kinds of large-scale challenges. »